
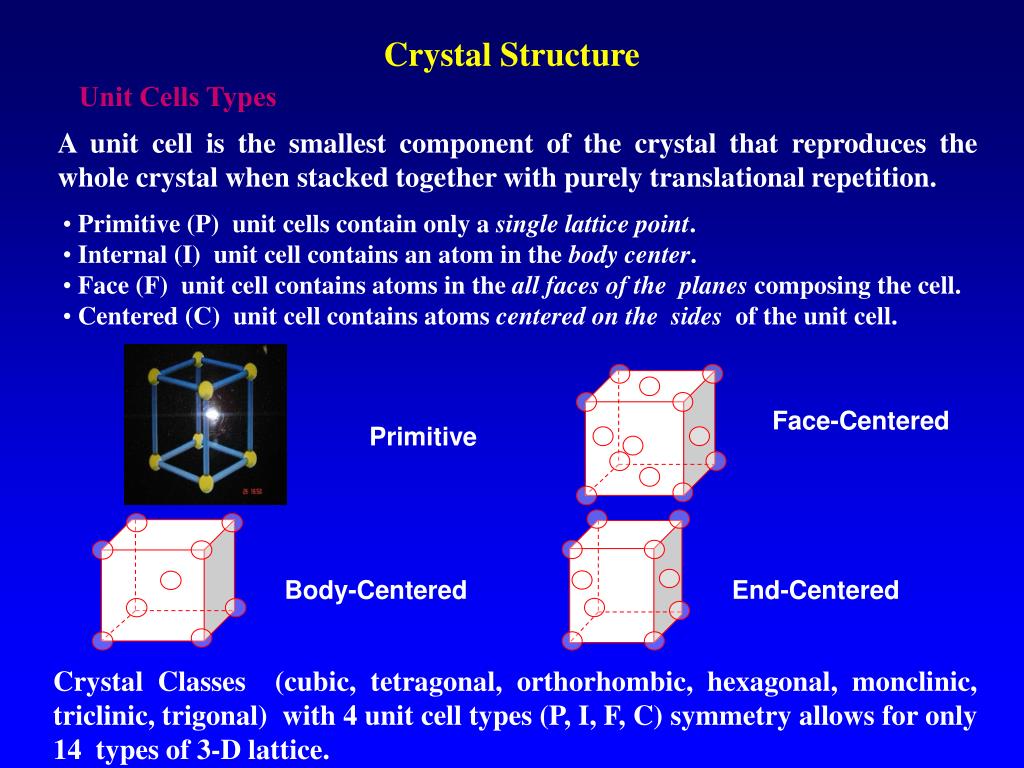
Adding impurities to crystalline solids to change their properties is called doping. Metal excess and Metal deficiency are the two types of this defect. (iii) Non-stoichiometric defects: When ratio of cations and anions changes as a result of the defect. Two types are Schottky defect and Frenkel defect. (ii) Stoichiometric defects: When ratio between cations and anions remains the same. (i) Any departure from perfectly ordered arrangement of constituent particles is called defect or imperfection. Packing efficiency = Volume of one atom Volume of the cubic unit cell × 100 % = 52. in the crystal are hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing. Packing efficiency = Volume occupied by 2 sphere sin the unit cell Total volume of the unit cell × 100 % = 68 % The Avogadros number of Barium atom in its body centered cubic lattice has to be. of atoms in unit cell M =Atomic mass a =Edge length (in cm)Ĭcp and hcp: Packing efficiency = Volume occupied by 4 sphere sin the unit cell Total volume of the unit cell × 100 % = 74 % Simple cubic r = a 2, Face centred cubic r = a 2 2, Body centred cubic r = 3 4 aĭensity of unit cell, d = Z × M a 3 × N A g c m - 3 (v) Relationship between radius (r) of an atom and edge length (a) The middle layer has 3 atoms which are sandwiched between the two layers, with tthe atoms snugly fit in the gaps of the atoms in the two layers. The lattice can be divided in three layers, with the top and bottom layers having atoms arranged in a hexagonal manner. The number of octahedral voids generated = N and the number of tetrahedral voids generated = 2 N This lattice is not cubic like the previous two. (iv) If the number of close packed spheres be N, then: (iii) Number of particles per unit cell of a cubic crystal (ii) Contribution by particles present at different positionsĬorner = 1 8, Face-centre = 1 2, Body-centre = 1, Edge-centre = 1 4 (f) Rhombohedral/Trigonal ( a = b = c, α = β = γ ≠ 90 ° ) 2 Windisch D and Becker P 1988 Lattice distortions induced by carbon in silicon Phil. (e) Triclinic ( a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90 ° ) One prerequisite for this is that the Avogadro constant, NA. (c) Orthorhombic/Rhombic ( a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = γ = 90 ° ) Crystal systems (types and characteristics): (iv) Classification of crystalline solids: Ionic, Molecular, Covalent/Network, MetallicĢ.

(iii) Classification of Solid: Crystalline (Regular arrangement of particles, anisotropic), Amorphous (No regular arrangement of particles, isotropic).
(ii) If intermolecular forces > thermal energy, substance exists as solid (i) Solid is the form of matter which possesses a definite shape and a definite volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
